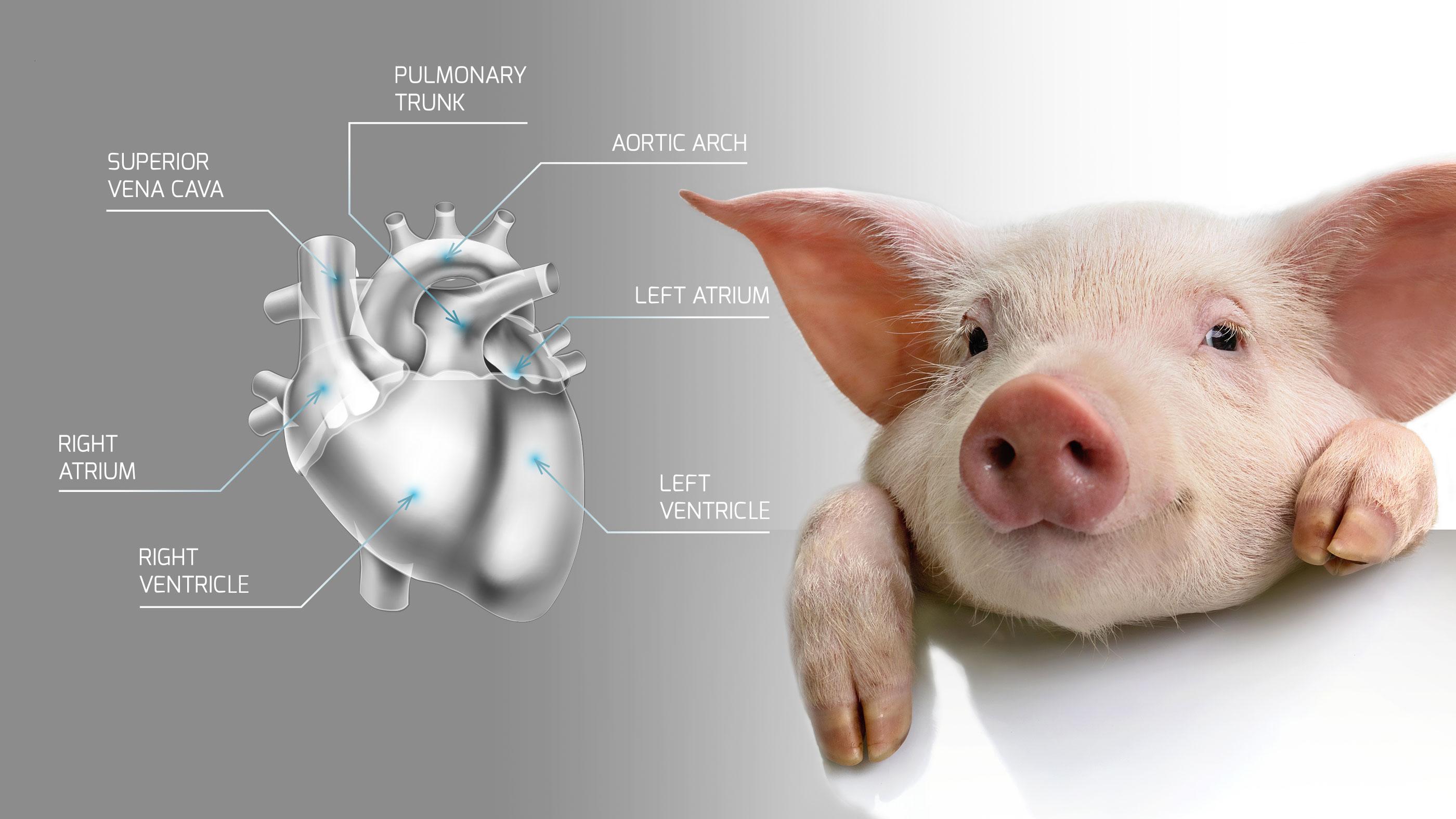
XTransplant's aim is to overcome the chronic shortage of human donor organs
-
SITUATION
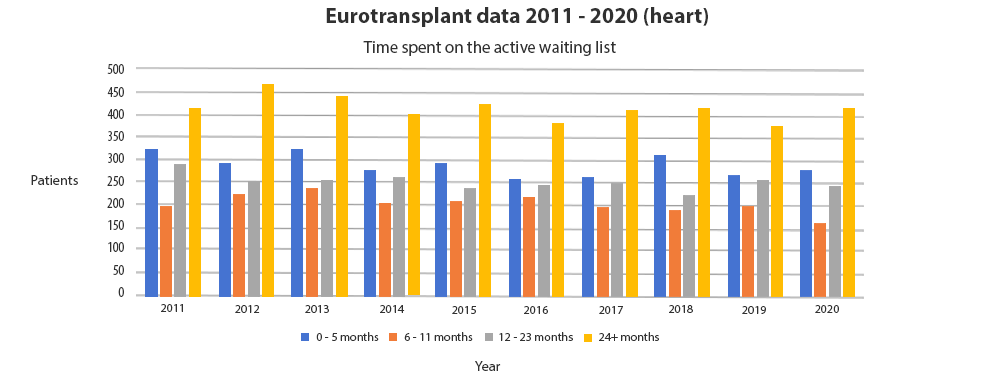
The number of available human organs donated is extremely limited while mechanical heart support systems are associated with complication and limited quality of life.
-
FACT 1

Heart diseases are still the leading cause of death worldwide.
-
FACT 2
The number of transplants required by far exceeds the number of donated organs.
-
FACT 3
High-urgency transplantation candidates are taken care 24/7 in hospitals.
-
FACT 4

Allotransplantation (human-to-human) is so far the only permanent therapy for patients with terminal heart failure.
-
FACT 5

The average waiting time for a heart transplant is currently more than one year.
-
FACT 6
The use of mechanical heart support systems is associated with high complication rates; the quality of life is limited.
XTransplant's approach and expertise

The Center for Innovative Medical Models (CiMM) at LMU Munich is a unique research environment for the generation, characterization and implementation of large animal models in biological and biomedical research. CiMM is a core infrastructure for a number of research networks, such as the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD), the DFG Transregional Collaborative Research Center 127 “Biology of Xenogeneic Cell, Tissue and Organ Transplantation – from Bench to Bedside “, and the EU H2020 Project iNanoBIT.
More information: www.lmu.de
XTransplant’s business model focuses at:
- Breeding of safe, durable and humanized genetically modified donor pigs involving external breeding facilities
- Organ Explantation and Transport in life-supporting devices to certified transplantation clinics
- long-term follow-up of patients including biobanking
From bench to bedside
-
XTransplant's Business Model
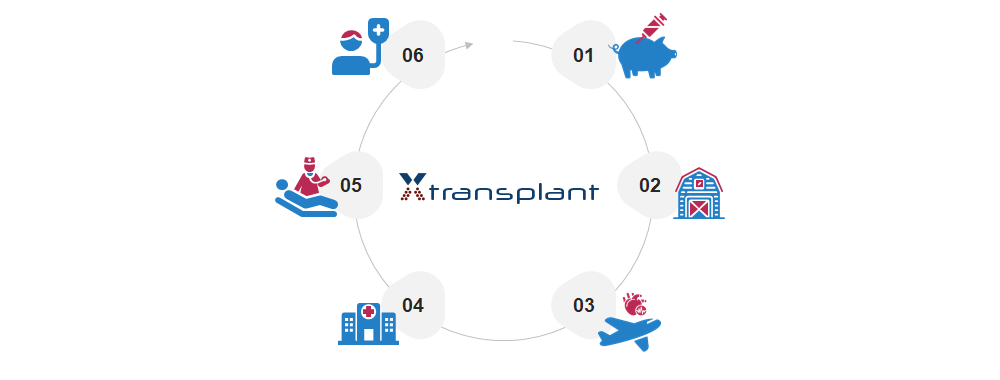
XTransplant's Business Model focuses at:
01 - Development of Patent-Protected Genetically Multi-Modified Donor Pigs
02 - Production of Donor Pigs under Designated Pathogen-Free (DPF) Conditions
03 - Organ Explantation and Organ Transport in Function-Preserving Perfusion Systems
04 - Organ Distribution Channels and Network of XTransplant-Certified Transplantation clinics
05 - Technical Support during Organ Implantation
06 - Clincal Follow-Up of Transplanted Patients and Biobanking -
01

Development of Patent-Protected Genetically Multi-Modified Donor Pigs
-
02

Production of Donor Pigs under Designated Pathogen-Free (DPF) Conditions
-
03

Organs Explantation and Organ Transport in Function-Preserving Perfusion Systems
-
04
Organ Distribution Channels and Network of XTransplant-Certified Transplantation clinics
-
05

Technical Support during Organ Implantation
Transplantation clinics and/or Health Care Insurances will reimburse for donor hearts and for services.
-
06

Clincal Follow-Up of Transplanted Patients and Biobanking